141. 环形链表
题目描述
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
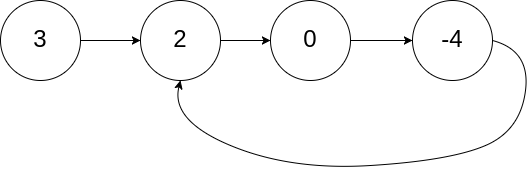
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:true 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
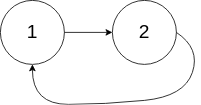
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0 输出:true 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:

输入:head = [1], pos = -1 输出:false 解释:链表中没有环。
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 104] -105 <= Node.val <= 105pos为-1或者链表中的一个 有效索引 。
进阶:你能用 O(1)(即,常量)内存解决此问题吗?
方法一:哈希表
我们可以遍历链表,用一个哈希表 true。否则链表遍历结束,返回 false。
时间复杂度
java
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return false;
}
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
if (set.contains(curr)) {
return true;
} else {
set.add(curr);
}
curr = curr.next;
}
return false;
}
}cpp
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode* head) {
unordered_set<ListNode*> s;
for (; head; head = head->next) {
if (s.contains(head)) {
return true;
}
s.insert(head);
}
return false;
}
};ts
function hasCycle(head: ListNode | null): boolean {
const s: Set<ListNode> = new Set();
for (; head; head = head.next) {
if (s.has(head)) {
return true;
}
s.add(head);
}
return false;
}python
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
s = set()
while head:
if head in s:
return True
s.add(head)
head = head.next
return False方法二:快慢指针
我们定义快慢指针
快指针每次走两步,慢指针每次走一步,不断循环。当快慢指针相遇时,说明链表存在环。如果循环结束依然没有相遇,说明链表不存在环。
时间复杂度
java
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}cpp
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while (fast && fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};ts
function hasCycle(head: ListNode | null): boolean {
let slow = head;
let fast = head;
while (fast !== null && fast.next !== null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow === fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}python
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
slow = fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
slow, fast = slow.next, fast.next.next
if slow == fast:
return True
return False